Table of Contents
The Economist as Scientist
The Scientific Method: Observation, Theory, and More Observation
Invention an economic theory is just like in other scientific fields, which is observation, summary to a theory and then collect data to test it. However, it is often difficult or impossible for economists to collect data because you cannot change policies just for experiments. Therefore, economists often pay attention to the natural experiments offered by history which can not only give insight into the economy of the past, but also allow to illustrate and evaluate economic theories of the present.
The Role of Assumptions
Make assumptions can simplify the question. e.g. once we understood the international trade in the simplified imaginary world, we are in a better position to understand international trader in the more complex world.
Also, the art in scientific thinking is deciding which assumptions to make. e.g. study short-run effect or long-run effect make different assumptions.
Economic Models
Economic models composed with graphs and equations which omit a lot of details to emphases the essence of economy. Each economic models make assumptions to simplify reality so as to improve our understanding of it.
Our First Model: The Circular-Flow Diagram
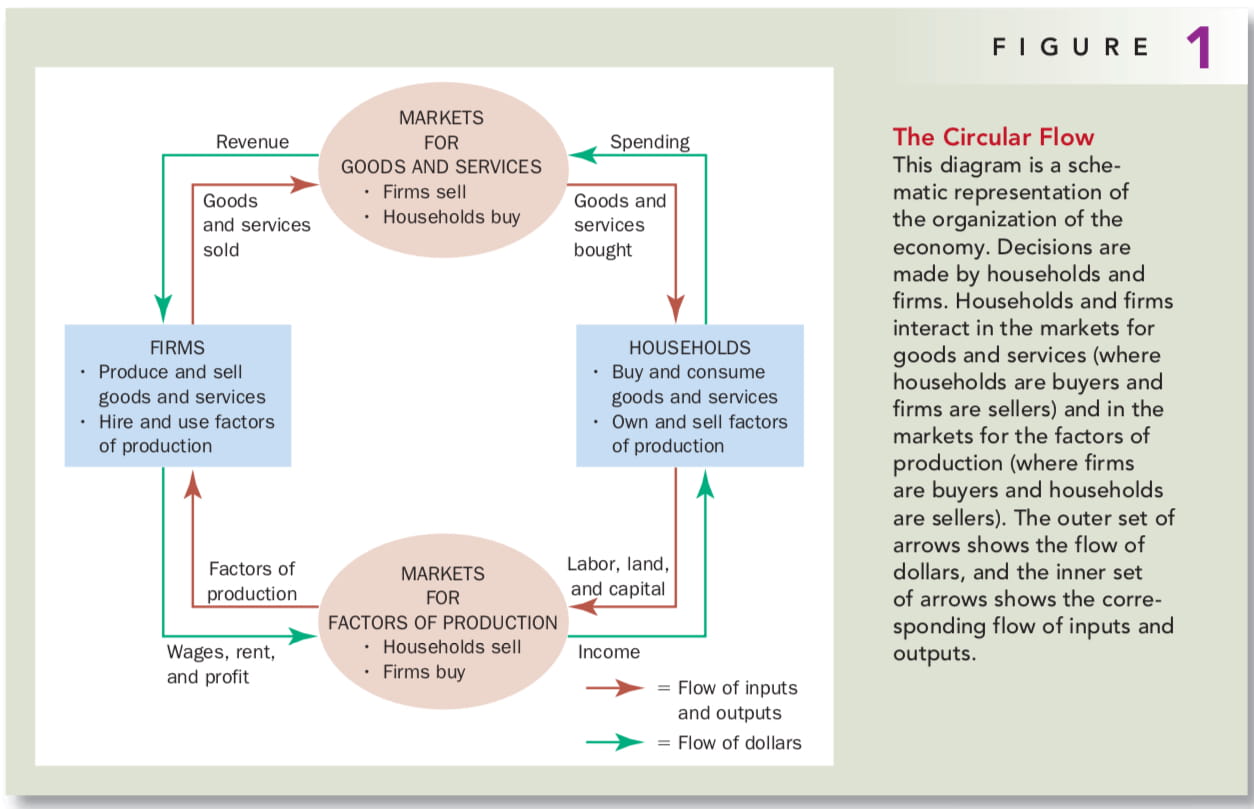
e.g. money in your wallet -> buy coffee in markets for goods and services (local Starbucks) -> revenue of the company -> pay rental or wage -> someone’s wallet
Because of its simplicity, this circular-flow diagram is useful to keep in mind when thinking about how the pieces of the economy fit together.
Our Second Model: The Production Possibilities Frontier
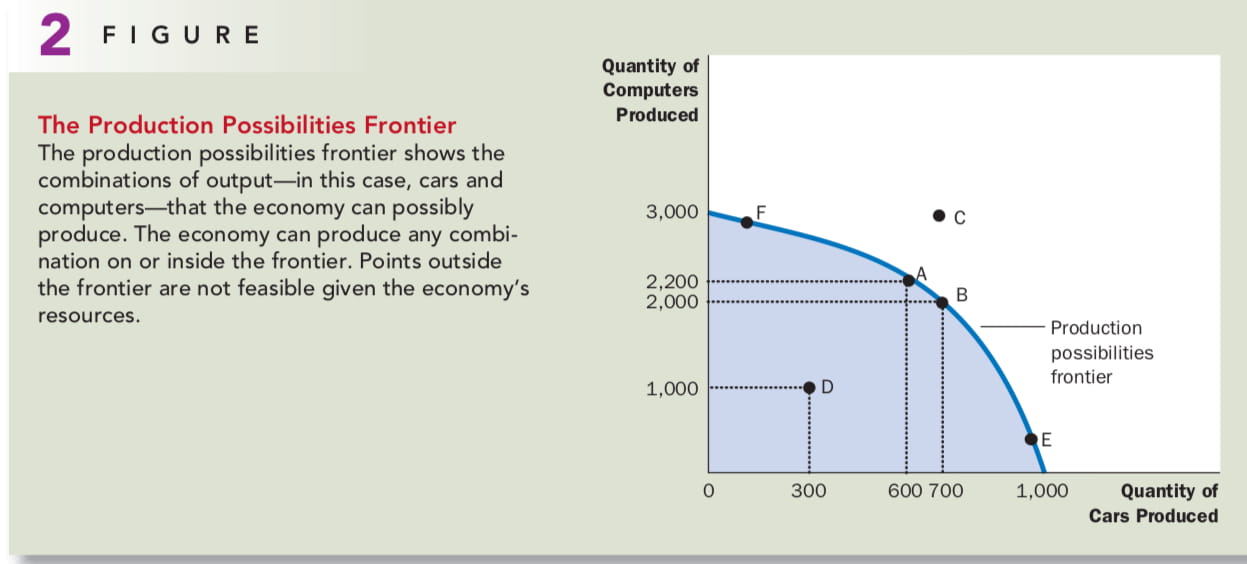 The production possibilities frontier shows the efficiency of the society. Because resources are scarce, not every conceivable outcome is feasible. Points on the production possibilities frontier represent efficient levels of production.
The production possibilities frontier shows the efficiency of the society. Because resources are scarce, not every conceivable outcome is feasible. Points on the production possibilities frontier represent efficient levels of production.
It also reveals trade-off and opportunity costs: if produce more computers, means have to produce less cars. The opportunity cost is measured by the slope of the production possibilities frontier, which means point F’s opportunity cost of a car is lower and point E’ opportunity cost of producing a car is higher. That’s because when at point E, the society has let all of car engineers to produce cars. Producing one more car means moving some of the best computer technicians out of the computer industry and making them autoworkers.
The production possibilities frontier also change with time, which shows economic growth. 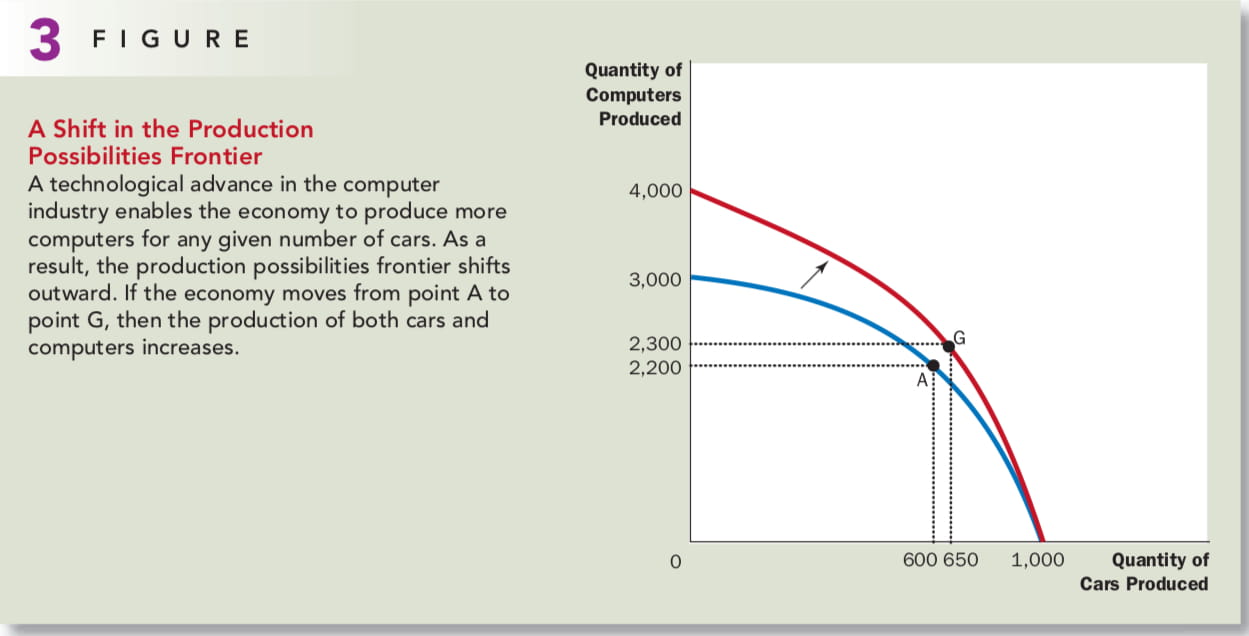
Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Economics is studied on various levels, which is traditionally divided into two broad subfields:
- Microeconomics is the study of how households and firms make decisions and how they interact in specific markets.
- Macroeconomics is the study of economy-wide phenomena, including inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
The Economist as Policy Adviser
Positive versus Normative Analysis
positive statements: claims that attempt to describe the world as it is normative statements: claims that attempt to prescribe how the world should be
Normative statements comes from positive statements as well as value judgements. Deciding what is good or bad policy is not just a matter of science. It also involves our views on ethics, religion, and political philosophy.
Economists in Washington
Economists in Whitehouse also face trade-offs. The influence of economists on policy goes beyond their role as advisers: Their research and writings often affect policy indirectly.
Why Economists’ Advice Is Not Always Followed
Economists offer crucial input into the policy process, but their advice is only one ingredient of a complex recipe.
Why Economists Disagree
Differences in Scientific Judgments
Economic is a young science and there is still much to be learned. They disagree because they have different hunches about the validity of alternative theories or about the size of important parameters that measure how economic variables are related.
Difference in Values
Economists give conflicting advice sometimes because they have different values.
Perception versus Reality
Why do policies such as rent control persist if the experts are united in their opposition? It may be that the realities of the political process stand as immovable obstacles. But it also may be that economists have not yet convinced enough of the public that these policies are undesirable.